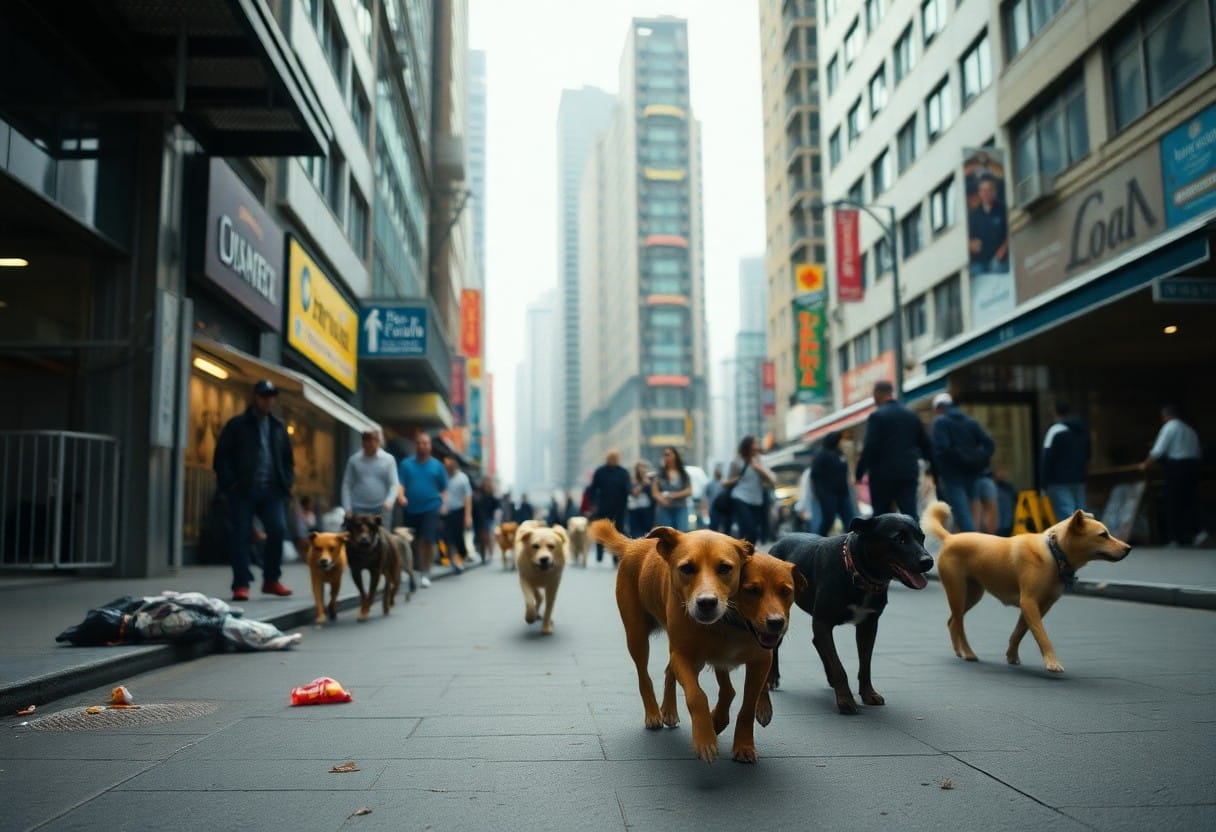
It’s vital for you to understand how urbanization significantly affects stray dog populations. As cities expand, they create both challenges and opportunities for these animals. Increased human activity often leads to greater abandonment rates, leaving many dogs to navigate urban environments on their own. However, urban areas can also provide shelter and resources that improve their chances of survival. This dynamic relationship between urban growth and stray dogs highlights the need for effective management and community awareness to address both the issues and potential benefits for these animals.
Key Takeaways:
- Population Growth: Urbanization often leads to increased human populations, which can result in higher stray dog numbers as more individuals abandon pets or fail to spay/neuter their animals.
- Resource Availability: Stray dogs benefit from urban environments due to the abundant food sources, shelter options, and access to waste, allowing populations to thrive despite their challenges.
- Health Risks: High stray dog populations in urban areas can pose health risks to both humans and dogs, including the spread of diseases and increased instances of dog bites.
Understanding Urbanization
Before plunging into the impact of urbanization on stray dog populations, it’s necessary to understand what urbanization entails.
Definition of Urbanization
Definition: Urbanization is the process through which rural areas transform into urban centers, characterized by increased population density and infrastructure development. This shift typically involves a movement of people from countryside to cities in search of better opportunities.
Historical Context
On the global landscape, urbanization has been an ongoing trend for centuries, driven by industrialization, technological advancements, and socioeconomic factors.
Hence, as societies evolved from agrarian to industrial economies, more individuals relocated to urban areas for work and improved living conditions. This shift marked a significant change in lifestyles, with cities rapidly expanding to accommodate growing populations. Significant milestones, such as the Industrial Revolution, further accelerated this trend, as urban areas became economic hubs attracting labor from diverse backgrounds.
Global Trends in Urbanization
Along with historical insights, it’s vital to consider contemporary trends in urbanization, which are reshaping cities worldwide, particularly in developing nations.
Urbanization is currently occurring at an unprecedented pace, with more than half of the world’s population now living in urban areas. Regions such as Asia and Africa are experiencing rapid urban growth, presenting both challenges and opportunities. As cities expand, you may witness an increase in infrastructure, services, and economic activity. However, this rapid transformation can also lead to issues like overcrowding, increased demand for resources, and a rise in stray animal populations, including dogs. Understanding these trends is vital for addressing the impact on both human and animal lives in urban settings.
Stray Dog Populations
Now, it’s vital to understand the various aspects of stray dog populations and their dynamics in urban settings. These populations often thrive in cities, leading to both benefits and challenges for communities.
Definition of Stray Dogs
Stray dogs are defined as canines that roam without an owner and are not actively cared for. They may be lost pets or abandoned animals, adapting to their environment as best they can.
Types of Stray Dogs
Stray dogs can be classified into several categories based on their behavior and interaction with humans:
- Owned strays: Pets that have become lost or neglected.
- Community dogs: Semi-domesticated canines that rely on local residents for food.
- Ferals: Dogs that have never been domesticated and have no socialization with people.
- Mixed breeds: A combination of different breeds that form stray populations.
- Females with litters: Moms raising puppies in unsupervised conditions.
After exploring the types of stray dogs, you can see how each category contributes uniquely to urban environments.
| Type | Description |
| Owned strays | Pets lost or abandoned by owners |
| Community dogs | Caring local support systems |
| Ferals | Dogs with no social interaction |
| Mixed breeds | Diverse hereditary traits present |
| Females with litters | Stray mothers raising puppies |
Dogs in these categories can pose challenges and create opportunities for communities. Each type holds its unique significance and influence on the local stray dog dynamics.
- Community involvement: Positive effects of local care initiatives.
- Public health concerns: Issues related to stray dog populations.
- Animal welfare: Rescue and rehabilitation efforts.
- Controversy: Varied opinions on managing these populations.
- Impact of urbanization: Changing landscapes affecting dogs.
After comparing these types, you gain insights into how urbanization shapes stray dog populations in ways that affect both animals and people.
Demographics of Stray Dog Populations
An understanding of demographics provides key insight into the overall composition and behavior of stray dog populations. Factors such as age, gender, and health status significantly impact the dynamics within these groups.
Consequently, the demographics of stray dog populations can reveal patterns such as high reproduction rates and the spread of diseases across regions. You may find that areas with limited veterinary care can see a rise in health issues among dogs, thereby putting both the canines and local citizens at risk. Dangerous behaviors from unspayed female dogs often lead to further increases in populations, while high mortality rates can occur during harsh conditions.
The Effects of Urbanization on Stray Dog Populations
Not surprisingly, urbanization significantly influences the dynamics of stray dog populations. As cities expand, various factors contribute to shifts in canine demographics, care, and community management. You may be wondering how these changes play out in real life. Let’s examine some critical aspects.
Increased Abandonment Rates
Between the bustling streets and the allure of urban life, many pet owners find themselves unable to provide for their dogs. This leads to higher abandonment rates. Unfortunately, as cities grow, these pets are often left to fend for themselves, resulting in a rising population of strays.
Food Availability and Urban Waste
Populations of stray dogs can thrive in cities primarily due to the abundant food availability created by urban waste. These areas often have plentiful food resources from discarded meals, overfilled trash bins, and scraps solicited from kind-hearted residents.
Indeed, the increase in urban waste provides stray dog populations with a surprisingly steady source of nutrition. As you walk through city streets, you may notice these dogs scavenging or foraging, which significantly reduces the pressure on their survival instincts. This optimistic aspect of urban life ironically supports the growth of the stray population, as they adapt to exploit available resources.
Changes in Habitat and Shelter
Between new buildings and increased human activity, the urban environment quickly reshapes the habitats available for stray dogs. Many have to adapt to less-than-ideal living conditions as the availability of natural shelters diminishes.
Food scraps are not the only concern; the adaptation to changing habitats involves a struggle for safety and shelter. Stray dogs often find refuge in alleyways, construction sites, or abandoned buildings. Unfortunately, these shelters are usually inadequate and expose them to harsh weather conditions and urban dangers. Your understanding of these environmental challenges can foster greater compassion for the resilience of these animals in the face of an evolving urban landscape.
Public Health and Safety Issues
Many cities face significant public health and safety issues as urbanization leads to growing stray dog populations. Stray dogs can pose various risks, including the transmission of diseases and increased rate of dog bites, both of which can impact community health and safety.
Zoonotic Diseases
Issues arise when stray dogs carry zoonotic diseases that can be transmitted to humans. These diseases, like rabies, can have severe consequences and require immediate medical attention, placing strain on local healthcare systems.
Bites and Attacks
With increasing encounters between stray dogs and people, the frequency of bites and attacks rises, leading to heightened concerns over safety in urban areas.
To mitigate this risk, it’s imperative to understand the circumstances that lead to biting incidents. Stray dogs often feel threatened or scared when approached, as they lack the socialization that well-kept pets receive. When you encounter a stray dog, it’s best to maintain your distance and avoid sudden movements that may provoke an attack. Educating the public about proper behavior around stray dogs is vital for personal safety.
Implications for Animal Control Policies
Any effective strategy to address stray dog populations must consider the implications for animal control policies. Communities need guidance on how to manage strays humanely and effectively, considering the existing public health risks.
A comprehensive approach to animal control is imperative for dealing with the stray dog issue. Policies should include spaying and neutering initiatives, responsible pet ownership education, and a robust rescue and adoption framework. By investing in these areas, you can help reduce the stray dog population sustainably, ultimately improving the health and safety of your community.
Social and Economic Impacts
Your understanding of the social and economic dynamics surrounding stray dog populations can help shape solutions for a growing issue in urban areas.
Community Perceptions of Stray Dogs
Behind the rising numbers of stray dogs lies a complex web of community perceptions. Many individuals view these dogs with fear and disdain, associating them with potential dangers such as bites or disease. On the other hand, some communities embrace these animals, seeing them as part of their cultural landscape. These varying attitudes can significantly influence local policies regarding stray dog management.
Economic Cost of Stray Dog Management
The financial burden of managing stray dog populations presents a significant challenge to urban areas. Local governments often allocate funds for animal control, sheltering, and public health initiatives to address the issues that arise from having a high population of strays.
In addition to direct costs, such as food, shelter, and veterinary services, there are indirect economic impacts related to lost tourism revenue, property values, and increased healthcare expenses from dog bites and rabies cases. Municipalities may find themselves struggling to balance these costs while trying to implement effective solutions for animal welfare and community safety.
Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
After recognizing the serious implications of stray dog populations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) often step in to provide imperative services. These organizations work to advocate for the humane treatment of strays, focusing on spaying, neutering, and vaccination initiatives.
Plus, NGOs can provide a critical support system for local governments by offering resources and outreach programs that educate the public on responsible pet ownership. Their efforts often help build community programs aimed at reducing stray populations sustainably while promoting animal welfare. Their involvement is vital in creating a long-term strategy that addresses both the social and economic factors at play in urban settings.
Case Studies
Once again, urbanization has led to various shifts in the population dynamics of stray dogs. Here are some compelling case studies that illustrate the relationship between urban growth and stray dog populations:
- Los Angeles, USA: An estimated 50,000 stray dogs roam the city due to a rapid increase in urban development. The city’s ongoing conflict between housing expansion and animal control efforts has exacerbated the situation.
- New Delhi, India: Approximately 35,000 stray dogs are currently living in its metropolitan area. Urbanization has pushed these dogs to populated regions, increasing the likelihood of human-animal conflicts.
- Istanbul, Turkey: A city with around 150,000 stray dogs, where urban sprawl has encroached on natural habitats. Public perception plays a key role in their management, with increased advocacy for humane treatment.
- Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Approximately 10,000 stray dogs inhabit the favelas, where urban expansion has sliced through their natural territories, resulting in rising calls for innovative intervention programs.
- Bangkok, Thailand: The population of stray dogs here is estimated between 70,000-100,000. Urbanization has exacerbated the issue, and local authorities have struggled to keep the numbers in check.
Stray Dog Management in Major Cities
Stray dogs in major cities often face numerous challenges as urban settings can lead to conflicts with humans and other animals. Your city might have organized management programs that include public awareness campaigns, sterilization initiatives, and animal rescue operations aimed at reducing stray populations while promoting humane treatment.
Successful Intervention Programs
Below are various successful intervention programs that have positively impacted stray dog populations worldwide. Numerous cities have adopted strategic measures to address this growing concern. Programs focusing on neutering and vaccination have shown significant results in areas like Istanbul and Los Angeles.
Another effective approach has been the implementation of community-based initiatives, enabling residents to participate in caring for and managing the stray populations. In cities like New Delhi, collaboration with non-profit organizations has led to a notable decrease in the stray dog population through targeted spaying and neutering. Education programs targeting locals about caring for and safely interacting with strays have also proven to improve public sentiment, ultimately alleviating the burden on animal shelters and reducing the number of strays populating busy urban areas.
Final Words
Summing up, you can see that urbanization significantly influences stray dog populations, leading to increased numbers and complex challenges for both communities and animal welfare. Your awareness of these factors can play a role in shaping effective policies and programs that address stray dog issues. By understanding the consequences of urban growth on these animals, you are better equipped to contribute to solutions that promote humane treatment and community engagement in managing stray populations.
Q: How does urbanization contribute to the increase in stray dog populations?
A: Urbanization often leads to a higher concentration of humans in one area, creating more opportunities for dogs to scavenge for food. The availability of waste from restaurants, parks, and residential areas can support larger dog populations. Additionally, as cities expand, natural habitats are reduced, forcing dogs to adapt to urban environments where they can reproduce more frequently, leading to an increased number of strays.
Q: What are the challenges associated with managing stray dog populations in urban areas?
A: Managing stray dog populations in urban settings presents several challenges, including limited resources for animal control, public safety concerns, and the need for effective spaying and neutering programs. Stray dogs can pose risks such as traffic accidents and potential aggression towards humans and other animals. Municipalities often struggle with balancing the welfare of the animals and the safety and concerns of residents, making effective management programs important.
Q: How can communities address the issue of stray dogs as urbanization continues to grow?
A: Communities can adopt multiple strategies to address the issue of stray dogs. This may include implementing spaying and neutering programs to manage reproduction rates, increasing public awareness campaigns about responsible pet ownership, and establishing partnerships with local animal shelters to facilitate adoption and rescue efforts. Creating dog-friendly spaces can also help accommodate the presence of dogs in urban settings, while promoting the importance of treating strays humanely.